Project
STEROPE aims to address decarbonisation challenges by demonstrating integrated
and sustainable value chains for advanced renewable fuels based on innovative carbon capture
and utilisation (CCU) technologies.
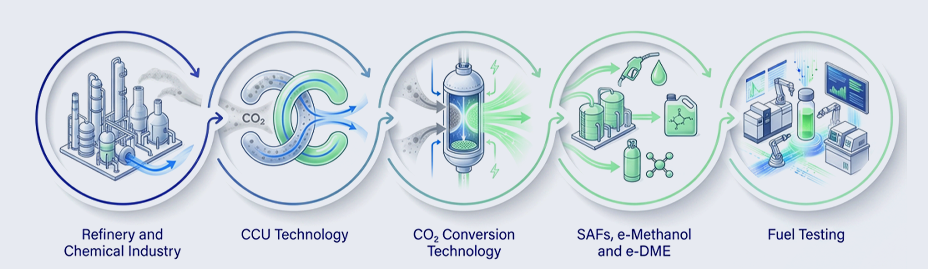
The project focuses on the efficient use of industrial CO₂, promoting circular economy principles,
industrial symbiosis and streamlined processes for energy-intensive applications, while validating solutions
under real refinery operating conditions.
Objectives
The main objective of STEROPE is to demonstrate the conversion of industrial CO₂ emissions into sustainable fuels for aviation and maritime transport through an integrated CCU value chain operating at refinery scale.

Demonstrate the conversion of industrial CO2 emissions into sustainable aviation fuels (SAF) and renewable marine fuels under real industrial conditions.

Design, build and operate a TRL7 demonstration plant, fully integrated into an operating refinery.

Advance circular economy and industrial symbiosis principles to improve resource efficiency in energy-intensive industrial processes.
Conduct Life Cycle Assessment (LCA), Techno-Economic Analysis (TEA) and social impact assessments to ensure environmental sustainability, economic viability and scalability.

Support regulatory validation of SAF and renewable marine fuels, enabling their uptake in real market applications.
Concept
Sustainable production of advanced renewable fuels from industrial CO₂ STEROPE demonstrates an integrated CCU process that converts industrial CO₂ emissions into advanced renewable fuels for aviation and maritime transport through a sequence of interconnected technologies, fully integrated into an operating refinery.
Integrated value chain and industrial symbiosis
By combining capture, conversion and fuel production within a single industrial site, STEROPE advances circular economy and industrial symbiosis principles, optimising resource use and enabling efficient integration into energy-intensive industrial environments.
Process
Sustainable production of advanced liquid fuels from industrial CO2 emissions
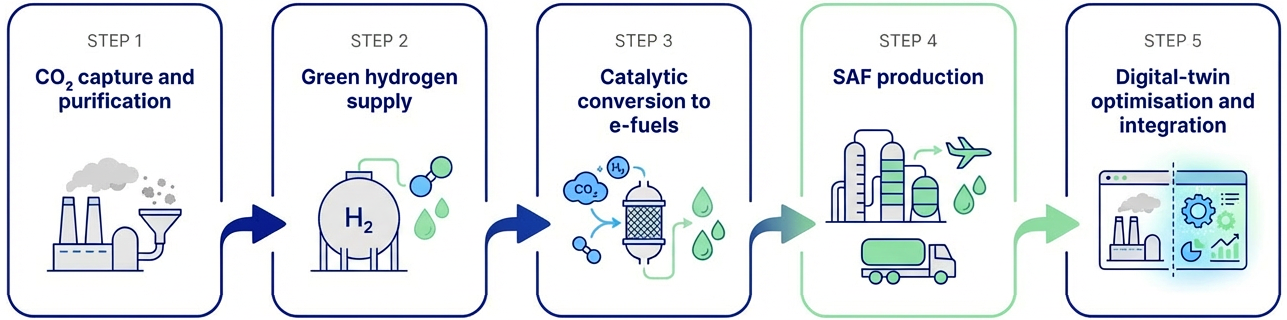
CO₂ is captured from refinery processes and purified using advanced capture technologies, reducing emissions from industrial operations and providing a reliable carbon feedstock.
Renewable hydrogen is produced and supplied to enable the synthesis of renewable fuels, ensuring low-carbon pathways and compliance with sustainability criteria.

Captured CO₂ and green hydrogen are converted through catalytic processes into e-methanol and e-DME, serving as renewable fuels and intermediates for maritime transport and further fuel upgrading.
Captured CO₂ and green hydrogen are converted through catalytic processes into e-methanol and e-DME, serving as renewable fuels and intermediates for maritime transport and further fuel upgrading.
A digital twin supports system optimisation, operational efficiency and safe integration within existing refinery infrastructure.
Expected impact
Decarbonising hard-to-abate sectors
STEROPE provides a scalable and replicable defossilisation pathway for aviation and maritime transport, two sectors that together account for approximately 2.5 % of global CO2 emissions and for which limited low-carbon alternatives are currently available.
By enabling the production of advanced renewable fuels from industrial CO2, the project directly supports compliance with ReFuelEU Aviation and FuelEU Maritime, facilitating the uptake of sustainable fuels in real market conditions.
Strong contribution to EU climate and energy goals
The project delivers renewable drop-in fuels aligned with EU climate neutrality objectives, energy security priorities and sustainable fuels strategies. By integrating CCU technologies at refinery scale, STEROPE strengthens Europe’s capacity to reduce dependence on fossil carbon while enhancing industrial resilience.
High mitigation potential
STEROPE technology shows a high CO2 mitigation potential, with the capacity to avoid more than 3.5 million tonnes of CO2 per year, assuming a 1 % EU market penetration in aviation and maritime transport.
This mitigation potential highlights the relevance of CCU-based fuels as a complementary solution alongside electrification and other decarbonisation pathways.
Industrial symbiosis & new revenue streams
By converting industrial CO2 emissions into high-value renewable fuels, STEROPE enables emitters to:
Unlock new revenue streams from CO2 utilisation.
Reduce exposure to carbon costs.
Adopt circular economy and industrial symbiosis models within existing industrial ecosystems.
Long-term economic impact
In 2040, widespread adoption of STEROPE-type solutions could:
Reduce CO2 emissions-related costs by up to 95 %.
Generate approximately €3 billion annually through a combination of fuel sales, technology licensing and carbon credit mechanisms.
Strategic innovation impact
STEROPE demonstrates an integrated SAF and e-methanol production system, generating robust technical, environmental and economic data essential for:
Future EU policy development, Investment decisions.
Research and innovation (R&I) actions in CCU and sustainable fuels.
Boosting EU technological leadership
Through collaboration with major industrial players, STEROPE reinforces Europe’s leadership in sustainable fuel innovation, strengthening competitiveness across the energy, refining, aviation and maritime value chains.
Advancement of technology readiness
By validating an integrated CCU-based fuel production system under real refinery conditions, STEROPE raises the technology readiness level (TRL) for e-SAF and e-methanol production, accelerating the pathway towards commercial deployment.